The medical models have become a critical component in modern health care education. Medical models are used in classrooms, laboratories and simulation centers, where abstract theory is transformed into the practical experiences that allow the student to learn by observing, touching and practising before he is introduced to actual patients. Accuracy, safety and measurable results of learning are the requirements of modern education, and medical models are able to meet the requirements as they involve connecting learning concepts to the practical, real-world tasks. Training institutions all over India are increasingly embracing simulation-based instruction to enhance student confidence, minimize mistakes and as well as to ensure uniformity in the educational standards.
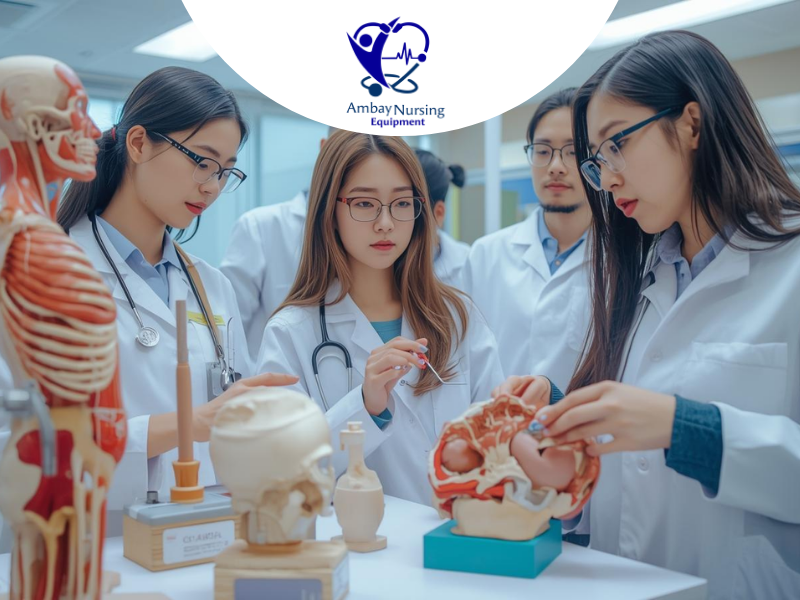

Table of Contents
How Simulation Enhances Learning
The best way to learn practically is to have students be able to touch on the subject matter. Medical models offer a systematic way to take an observation to performance. Students examine the anatomy and repeat the processes and combine theory and clinical thinking. Since medical models recreate natural anatomy and pathways of a procedure, they enable practice repeatedly without time constraints and patient risk. This rehearsal enhances retention, high technical accuracy, and anxiety reduction in the process of clinical exposure. Medical models can also be employed in objective assessment when used regularly, as they give instructors a chance to measure technique, hygiene, and procedural flow accurately.
Transformation of Classrooms Through Medical Models in Education
Medical models for education in academic setup transform education to learners who listen to education rather than participate in studying. Students break down anatomy parts, follow vascular systems, and discover the structural landmarks, which cannot be easily visualized by means of textbooks. This is a sense of learning that enhances spatial awareness and conceptual clarity. Medical models for education are used by educators in lectures, tutorials, and independent studies to modify explanations to diverse learning styles. Standardized outcomes are also experienced in institutions that use medical models for education since all students receive equal exposure irrespective of the number of students in a particular class. Recurrent uses of medical models for education boosts vocabulary, anatomical associations and simplify difficult topics.
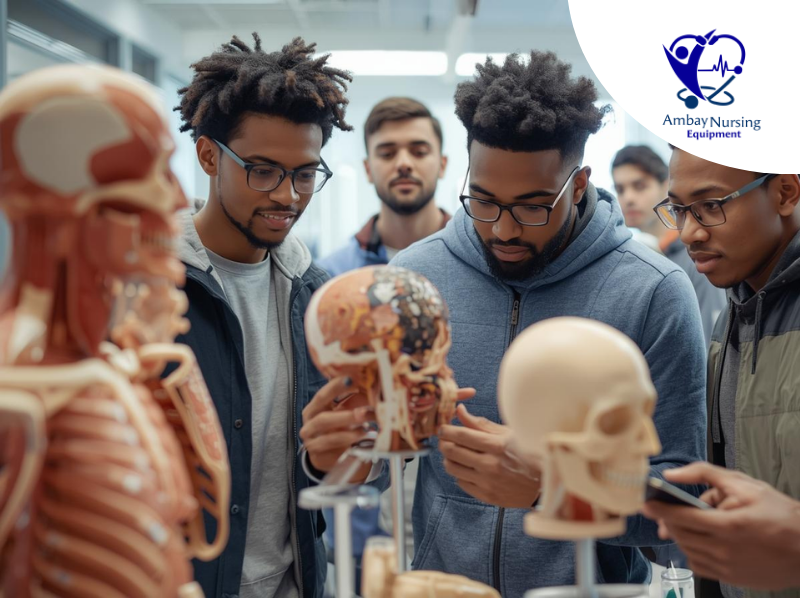
Development of Technical Proficiency Under Medical Models of Medical Training
Development of skills needs a secure way to practice, correct and repeat. That foundation is offered by medical models for medical training. Skills laboratories are conducted by the trainers showing the steps performing a certain procedure using medical models for medical training, and the trainee may receive immediate feedback and correct mistakes. The integration of medical models for medical training early on minimizes the learning curve and the amount of procedural errors made during the hospital posting. The perpetuation of medical models for medical training facilitates uniformity of practices between batches and prepares an individual to work under supervision.

Enhancing Nursing Competence via Medical Models of Nursing Training
Precision, empathy, and responsiveness are the three aspects that are emphasized in nursing education. Medical models for nursing training are simulations of real patient care activities, including medication administration, catheterization, wound care, and monitoring. These tools can be used to allow learners to practice the techniques without violating patient dignity and safety. Based on guided simulations, nursing students acquire the skills of communication, teamwork, and situational awareness. Graduates exhibit confidence and clinical preparedness when medical models for nursing training are instituted within the institutions during the coursework. Medical models for nursing training through regular drills also support infection control, documentation practice, and ethical responsibility during professional practice.
Improvement of Decision-Making Medical Models for Clinical Skills
Clinical competence is a capacity to act accordingly in diverse circumstances. Medical models for clinical skills reproduce clinical settings of examination and treatment where students get to practice in the evaluation, diagnosis and treatment of patients. Case-based scenarios based on medical models for clinical skills involve instructors presenting learners with complications, prioritization problems, and protocol-based reactions. Such controlled environments promote critical thinking and give corrective feedback at the same time. Having the experience of being exposed to the medical models for clinical skills repeatedly, the students develop judgment, efficiency, and professional composure, which leaves them ready to meet unpredictable clinical needs.
Making Anatomy Simple with Medical Models for Anatomy Learning
Anatomy is the foundation of healthcare education that is viewed as a complicated subject. Medical models for anatomy learning render abstractions into three-dimensional reality. The medical models for anatomy learning allow students to remove parts, view layered systems and learn about spatial changes amongst organs, and students can distinguish between normal variations and pathological changes. The consistent application of medical models for anatomy learning improves long-term memory, develops diagnostic thinking, and equips students with subjects of advanced clinical importance, which demand the precision of anatomy.
Quality Standards and Institutional Reliability
The effectiveness of education is based on the quality and reliability of training equipment. Good medical models include just proportions and hard materials, and the representation of the anatomy is consistent across different medical models. Suppliers like Ambay Nursing Equipments, which have a good reputation, come up with models that can be used in intensive classes without compromising on anatomical integrity. Long-term stability, low replacement costs, and standardization of teaching results that meet academic standards are the advantages of investing in high-quality medical models among the institutions.
Patient-Centered Training, Ethics, and Safety
Ethical learning cultures focus on patient wellbeing. Medical models enable students to learn to make errors, repeat, and fine-tune techniques without endangering the safety of patients. Working on medical models helps build a sense of respect towards hygiene standards, consent, and professional boundaries. This strategy creates an ethical awareness and minimizes the chances of making mistakes when the actual patients are concerned to a large extent.
Technology Integration and Future Preparedness
With the digitalization of healthcare and the introduction of minimal invasive surgeries, education should also change. Medical models can be utilized as the initial step of progressive learning to equip students with advanced simulation and technology-aided practice. Those institutions that include high quality medical models will make sure that the students learn the best techniques prior to graduating and joining digital or robotic models. The suppliers such as Ambay Nursing Equipments have remained in facilitation of this transformation through provision of training solutions that are in tandem with the new medical curricula.
Economical and Long-term Educational Benefit
Medical models have long-term cost advantages despite the initial investment that will need planning. They are reusable and durable; hence they do not rely on live demonstrations and eliminate risky training. Improved student performance increases the reputation and employability of the institution. Collaboration with Ambay Nursing Equipments offers colleges with reliable training tools that can assist them in providing consistent teaching and long educational payoff.
Conclusion
Medical models have brought a change in the education of healthcare through the integration of realism, safety and measurable outcomes. By incorporating medical models for education, medical models for medical education, medical models for nursing education, medical models for clinical skills, and medical models for anatomy learning, institutions provide systematic, ethical and future education. Cooperation with trusted suppliers like Ambay Nursing Equipments would guarantee the availability of long-lasting anatomically correct instruments that maintain the academic standards. With the further development of healthcare education, medical models will still be the center of the formation of competent, confident, and patient-focused specialists.
FAQs
Q1. What are the purposes of medical models in education?
Anatomy, procedures and clinical decision-making are taught using medical models that cover learning in a practical and hands-on way.
Q2. What is the role of medical models in education among students?
Medical models for education enable the learner to get in contact with the structures directly which enhances the visualization, retention and clarity of concepts.
Q3. Why are medical models of medical training necessary?
Medicine models for medical training offer safe practices of being able to practice the same thing and enabling fewer technical errors and growth in technical confidence.
Q4. What do medical models of nursing training contribute to nursing students?
Simulating real patient care tasks with medical models for nursing training helps to reinforce skills and communication and responsibility with the profession.
Q5. How do the medical models for clinical skills contribute to competence building?
Medical models for clinical skills simulate clinical examination and treatment situations to enhance judgment, accuracy, and clinical responsiveness.
Q6. What are the effects of medical models for anatomy learning on long-term knowledge?
Medical models for anatomy learning display three-dimensional systems that develop and strengthen the memory and diagnostic arguments.
