The current healthcare world requires accuracy, explicitness and practice opportunities that are realistic in nature. This is the reason why organizations all over the globe invest in various forms of medical models that can support both theoretical education and actual clinical training. All categories have a specific role to play, and students are able to develop competence in anatomy, procedures, patient care, and emergency response. The following is a systematic and thoroughly developed description of the significant categories of medical models, arranged in a manner such that it aids the educators, students and healthcare training institutions to make well-informed choices.
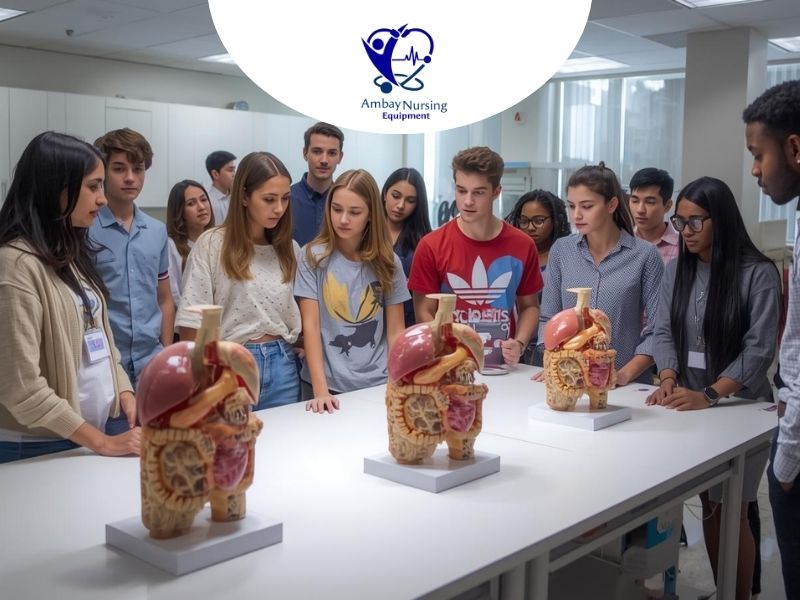
Table of Contents
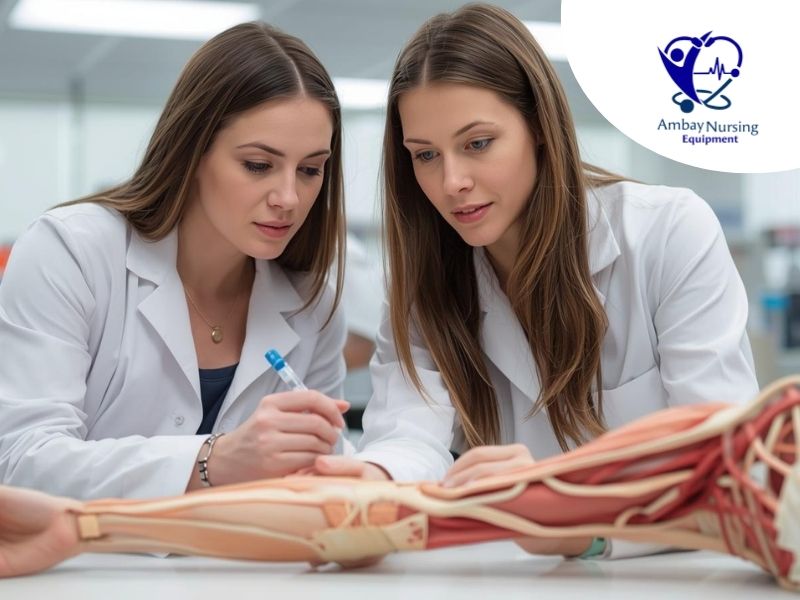
Anatomical Medical Models
The basis of medical and nursing education is anatomical medical models. These models are created to imitate the human body with amazing precision and the student can be able to visualize the structures that cannot easily be described with books only. These models offer three-dimensional depiction of organs, tissues and systems, which is essential in developing initial conceptual knowledge.
Common types include:
- Full Skeletal Models – Models that are used to examine all the major bones, joints and the supporting structures. These are what can assist learners to be aware of landmarks that are vital in processes like injections, physiotherapy, and orthopedic assessment.
- Organ-Specific Models – The models of the heart, lungs, liver, kidneys, stomach, and the brain. Such models can be equipped with parts, which can be removed to reveal inner layers.
- System Models – Elaborate models depicting the circulatory pathways, digestive systems, respiratory systems, sexual organs and the structure of the nervous system.
- Sectional Models – Slices through organs that assist the students learn about the process of disease, the presence of tissues and their spatial orientation.
These medical models reinforce the knowledge of anatomy, enable students to memorize complicated areas, and facilitate later semester clinical training.
Clinical Skill Training Models
After they are introduced to the fundamentals of anatomy, students need to train clinical skills. This is where the medical training models are provided. These simulators represent the human tissue, skin textures and procedure reactions, providing the learners with a real-life scenario where they can practice the techniques safely.
Examples include:
- Vein and Injection Arms – These arms have built-in veins and can be used to teach students about cannulation, venipuncture and the use of medications. They simulate natural vascular resistance and flashback, and they assist students to gain confidence.
- Catheterization Models – This simulator model uses male and female simulators to educate nurses on urinary catheter insertion, care and troubleshooting.
- Airway Management Models – The models are invaluable to paramedics and models for nursing students who are being taught how to perform intubation, suction and simple airway clearance.
- Wound Care Models – In these, parameters such as simulated burns, lacerations, ulcers, and infections are incorporated so that the learners can practice dressing change, wound assessment, and emergency bandaging.
These medical models empower skillfulness, decrease clinical malpractices and equip the students to act on actual patients without feeling afraid or hesitant to do so.
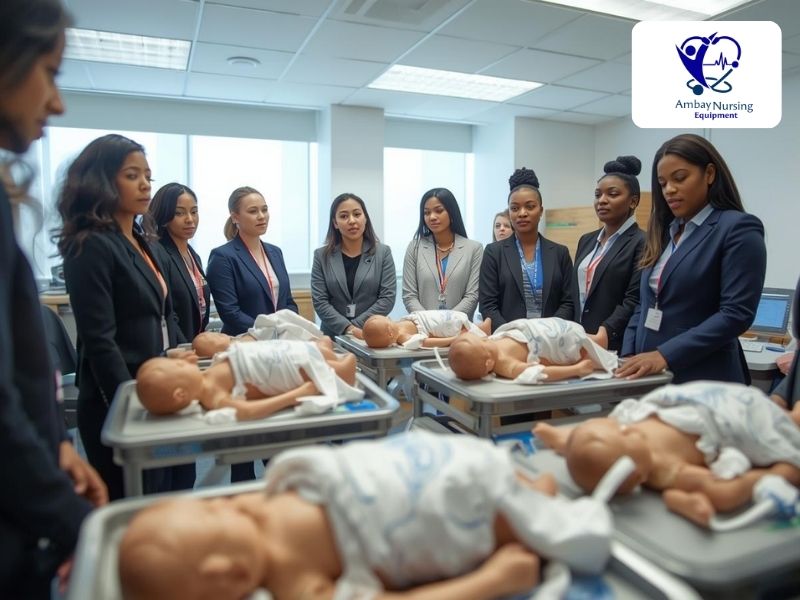
Full-Body Nursing Manikins
Full-body manikins are a whole patient and therefore, are quite essential to nursing colleges, hospitals and simulation laboratories. These medical models enable students to train on a broad assortment of clinical activities within a realistic and controlled environment.
Key types include:
- Basic Nursing Manikins – This is based on day-to-day patient care, and practices washing, positioning, feeding, oral care, bed preparation, and vital signs training. They are applied across the first year in nursing programs.
- Advanced Nursing Manikins – They have features such as heart sounds, lung expansion, palpable pulses and sensor-based feedback. They assist learners to comprehend clinical alterations in times of emergencies.
- Pediatric and Neonatal Manikins – Are infants and children, and assist in acquiring neonatal resuscitation, pediatric assessment, thermal regulation, and infant care routine skills.
Complete medical models are also necessary in simulation-based learning where students can apply real-life situations like cardiac arrest, trauma, falls, or acute worsening.
Gynecological and Obstetric Medical Models
Special training on maternity, midwifery, and gynecology programs is backed by these models. They assist the students to rehearse mothering, reproductive anatomy, childbirth methods and prenatal check-ups.
Major types include:
- Birthing Simulators – Show phases of labor, position of the fetus, dilation of the cervix, and delivery mechanisms. Students are taught how to handle normal and complicated deliveries.
- Pelvis Examination Models – These are training models that train on the use of the speculum on the insertion, the cervical examination, practicing on the Pap smear and locating the structures of the reproductive organs.
These medical models help to gain insights of female anatomy and provide safe and competent care in the events surrounding maternity.

Emergency and Trauma Medical Models
Emergency medicine is a field that demands immediate thinking, good technical expertise, and pressure responses. Medical models are emergency specific and enable trainees to undergo realistic situations in terms of injury or life-threatening situations.
Common examples include:
- Hemorrhage Control Trainers – Artificial bleeding lines on the model, which replicate the venous or arterial flow, can be used to instruct the learners how to apply pressure, pack a wound, and use hemostats.
- Choking Simulators – Permit practice in the abdominal thrusts, back blows, and removal of airway obstruction.
- Trauma Models- Fractures, burns, extremely lacerated, and penetrating injuries are all included in the paramedic and emergency-care education.
- CPR Manikins – They offer real time feedback about the compression depth, ventilation and timing to master resuscitation techniques.
These medical models provide a high-pressure learning environment that resembles the actual emergencies and keeps the trainees safe.
Specialty Medical Models
They are very specialized models that advocate niche spheres of healthcare education. They provide high-level specifications on specific medical fields.
Types include:
- Dental Models – These are used to learn how to brush, remove plaque and clean cavities and carry out the practices of orthodontics.
- Ophthalmology models- These have elaborate eye structures, which one can study the retina, optic nerve, movement of the lens, as well as the pattern of diseases.
- Dermatology Models – Demonstrate the rashes, lesions, infections, and other skin disorders.
- Orthopedic Models – These are fractures, joint motions, ligament designs and prosthetic positions exemplified by surgery models.
These medical models are designed to meet the postgraduate training, specialty courses and laboratory demonstrations.
Patient Handling and Care Models
These models are the most basic building blocks of nursing, which is caring about patients in a safe and empathetic manner. They assist learners to learn more about the ergonomic methods and necessary bedside procedures.
Popular examples:
- Bedridden Patient Models – These models are used to instruct on turning, transferring, repositioning, fall prevention, and comfort measures.
- Elderly Care Models – Recreate age-related conditions, e.g. inability to move, frailty of skin, mental decline.
- Communication Simulators – The state-of-the-art manikins can talk, blink, or be touched, and are used to teach students how to interact with the patient and support his or her feelings.
These models are the most basic building blocks of nursing, which is caring about patients in a safe and empathetic manner. They assist learners to learn more about the ergonomic methods and necessary bedside procedures.
Such medical models render the everyday patient care training more humane, realistic, and effective.
Interactive Medical Models, Simulation Based
Another rising trend in contemporary training settings is interactive, technology-based medicine models which mix physical design with digital additions. The upgraded models for nursing students to have a feel of real-time feedback and thus make their training more result-oriented and effective. The models are currently being incorporated into high-level simulation labs by many institutions to provide a more comprehensive learning environment.
Some of the most common interactive models are:
- Sensor-Enabled Manikins – They also include in-built monitors that monitor compression depth, the volume of ventilation, pulse detection, and even airway pressure. They can be of great use in CPR, neonatal resuscitation and advanced cardiac life support training.
- Virtual-Augmented Hybrid Models – These medical models are physical anatomical models with augmented reality overlay. Tablets or headsets can help students to see internal organs, trace the circulation or analyze bodily systems.
- Scenario-Driven Patient Simulators– It is possible to make these manikins to resemble symptoms like difficulty in breathing, cyanosis, sweating, or irregular heart sounds. They enable teachers to create clinical scenarios on which learners are required to diagnose and treat in real practice.
- Telemetry-Based Skill Models – These provide wireless monitoring in the process of injections, catheter handling, and airways insertion. The feedback is shown on the external screens, which provides learners with an immediate opportunity to fix their technique.
Interactive medical models will improve decision-making, increase the measurability of assessments, and prepare students to work in technology-driven hospitals of the future.

Conclusion
The variety of medical models in the present day is enormous and widespread with each category having its specific purpose of training the next generation of medical practitioners. Through detailed anatomical models up to the sophisticated simulation manikins, students are assisted to achieve accuracy, confidence and competence with any model. When the correct combination of these models is incorporated into their program, institutions are guaranteed that the learners acquire the skills required in the real world when attending to the patients, clinical judgment, and growth of the profession.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), strong healthcare systems rely on a well-trained and skilled health workforce, including nurses, doctors, and other healthcare professionals. The WHO Health Workforce team supports countries by providing guidance, data, and strategies to help improve training, availability, and overall quality of healthcare workers.
FAQ's
Q1. What is the use of medical models?
Medical models assist students to study anatomy, practice, and develop clinical skills in the most feasible way.
Q2. What are the important medical models that the beginners need?
Anatomical medical models such as skeletons, organ replicas and system-based models are primarily used by beginners.
Q3. Do medical models enhance clinical accuracy?
Yes, they provide repetitive practice, which allows the students to do procedures with higher accuracy and confidence.
Q4. Do we need full-body manikins in nursing training?
Full-body medical models are necessary since they replicate the actual patient care and emergency situation.
Q5. What are the ways in which institutions select the appropriate medical models?
Before choosing the right models, they take into consideration quality, realism, curriculum requirement, and durability.
